A group of Russian-state hackers known for almost exclusively targeting Ukrainian entities has branched out in recent months, either accidentally or purposely, by allowing USB-based espionage malware to infect a variety of organizations in other countries.
The group—known by many names, including Gamaredon, Primitive Bear, ACTINIUM, Armageddon, and Shuckworm—has been active since at least 2014 and has been attributed to Russia’s Federal Security Service by the Security Service of Ukraine. Most Kremlin-backed groups take pains to fly under the radar; Gamaredon doesn't care to. Its espionage-motivated campaigns targeting large numbers of Ukrainian organizations are easy to detect and tie back to the Russian government. The campaigns typically revolve around malware that aims to obtain as much information from targets as possible.
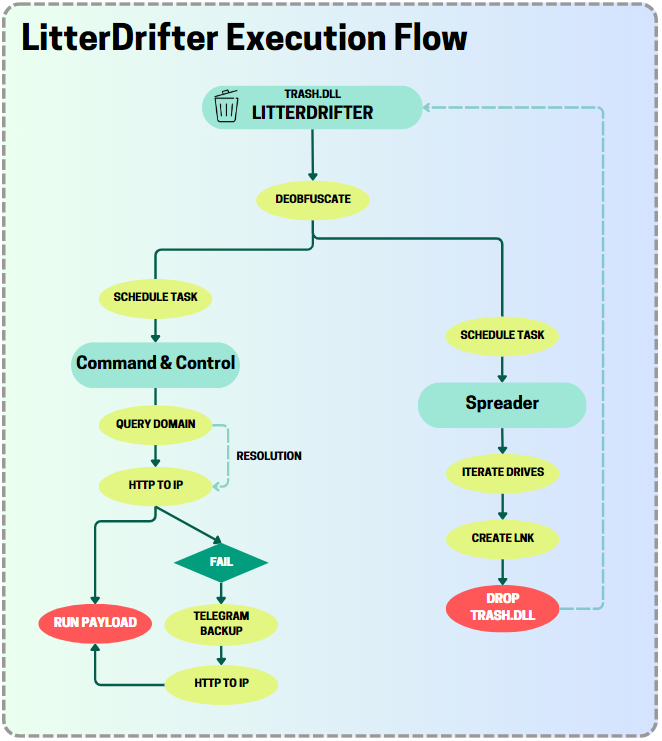
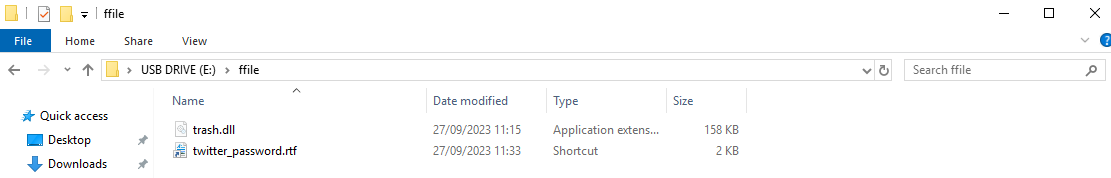
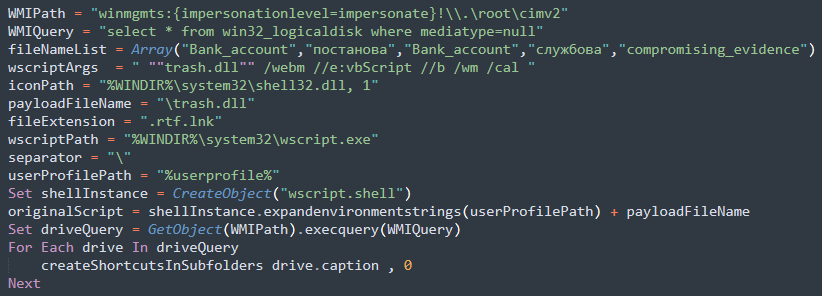
One of those tools is a computer worm designed to spread from computer to computer through USB drives. Tracked by researchers from Check Point Research as LitterDrifter, the malware is written in the Visual Basic Scripting language. LitterDrifter serves two purposes: to promiscuously spread from USB drive to USB drive and to permanently infect the devices that connect to such drives with malware that permanently communicates with Gamaredon-operated command-and-control servers.
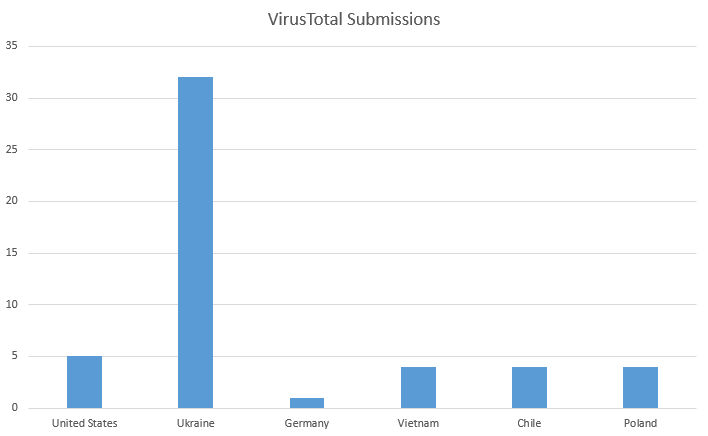
“Gamaredon continues to focus on [a] wide variety [of] Ukrainian targets, but due to the nature of the USB worm, we see indications of possible infection in various countries like USA, Vietnam, Chile, Poland and Germany,” Check Point researchers reported recently. “In addition, we’ve observed evidence of infections in Hong Kong. All this might indicate that much like other USB worms, LitterDrifter [has] spread beyond its intended targets.”
The image above, tracking submissions of LitterDrifter to the Alphabet-owned VirusTotal service, indicates that the Gamaredon malware may be infecting targets well outside the borders of Ukraine. VirusTotal submissions usually come from people or organizations that encounter unfamiliar or suspicious-looking software on their networks and want to know if it’s malicious. The data suggests that the number of infections in the US, Vietnam, Chile, Poland, and Germany combined may be roughly half of those hitting organizations inside Ukraine.


 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
